
If you’re not yet familiar with the term, in the intricate landscape of web development and search engine optimization (SEO), understanding the significance of the “noindex” directive within the robots meta tag is paramount for webmasters. Embedded within the HTML source code of web pages, the robots meta tag provides instructions to search engine crawlers on how to interact with and index content. When webmasters need to fix issues related to indexing or control the visibility of specific pages, the “noindex” directive becomes a critical tool in their arsenal.
The “noindex” directive serves as a powerful mechanism for webmasters to prevent search engine crawlers, such as Googlebot, from indexing certain pages or content on their website. By strategically deploying the “noindex” directive, webmasters can effectively hide pages from search engine results pages (SERPs), ensuring that sensitive or irrelevant content does not appear to users searching online. This directive also complements other directives like “nofollow,” which instructs search engine bots not to follow links on a page, thereby sculpting the flow of PageRank and enhancing the site’s overall SEO strategy.
In digital marketing and website management, mastering the implementation of the robots meta tag, alongside its counterpart, the ‘X-Robots-Tag’ HTTP header, is essential. The ‘X-Robots-Tag’ header offers a more advanced approach to setting directives at the HTTP level, providing webmasters with granular control over indexing behavior. Furthermore, tools like Google’s URL Inspection enable webmasters to validate and analyze how search engine crawlers interpret these directives, empowering them to fine-tune their website’s indexing settings for optimal performance.

For bloggers and content creators, the “noindex” directive within the robots meta tag plays a crucial role in managing the visibility of individual posts or pages. By selectively applying the “noindex” directive, bloggers can maintain control over which content appears in search results, shaping their online presence and maximizing the impact of their digital marketing efforts. Additionally, understanding how to combine the “noindex” directive with other directives like “disallow” or “nonindex” meta tags enhance the effectiveness of website optimization strategies, ensuring that webmasters can navigate the complexities of SEO with confidence and precision.
To remove the ‘noindex’ tag directive from the ‘robots’ meta tag in a WordPress website, you can follow these steps:
Table of Contents
1. Check your SEO plugin settings
If you are using an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO, All in One SEO, or Rank Math, check the plugin settings to ensure that the ‘noindex’ directive is not being added by the plugin. These plugins often have options to control the robots.txt file meta tag for individual pages or the entire site.
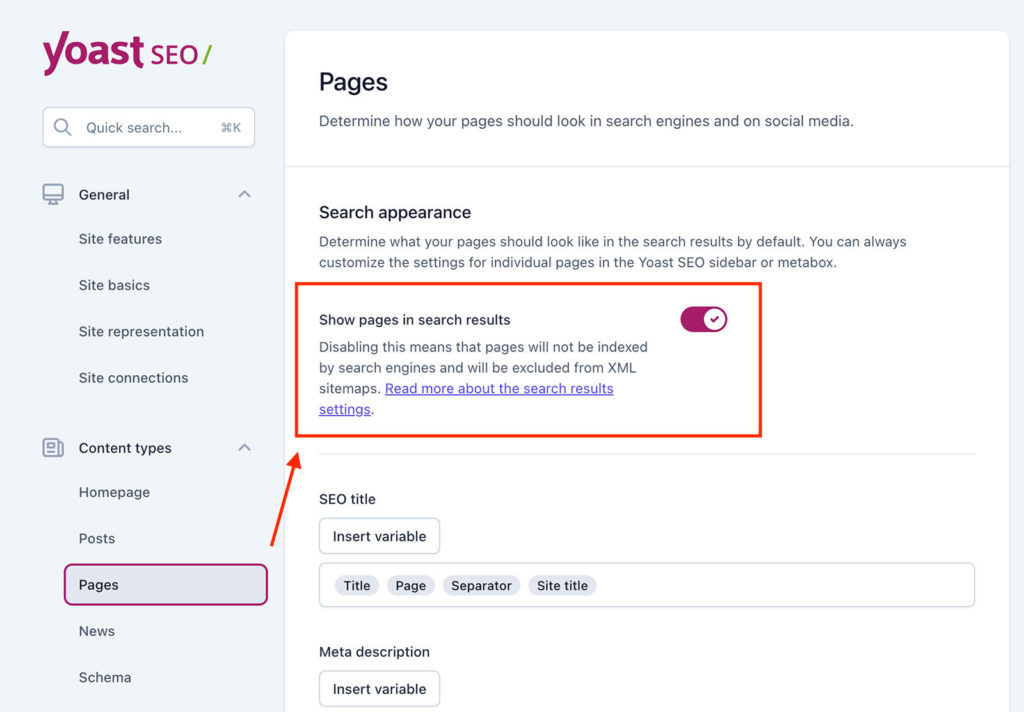
For example, in Yoast SEO:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard,
- click on ‘SEO‘ in the sidebar,
- and then select ‘Search Appearance.‘
- In the ‘Content Types‘ tab,
- find the content type (e.g., Posts or Pages) with the ‘noindex‘ directive
- and set the ‘Show [content type] in search results?‘ option to ‘Yes.‘
- If you want to change the setting for an individual page or post, edit the page or post, scroll down to the Yoast SEO meta box,
- click on the ‘Advanced‘ tab,
- and set the ‘Allow search engines to show this [content type] in search results?‘ option to ‘Yes.‘
2. Check your theme’s header.php file
Some WordPress themes may add the ‘noindex’ directive in the ‘robots’ meta tag by default. To check and remove it:
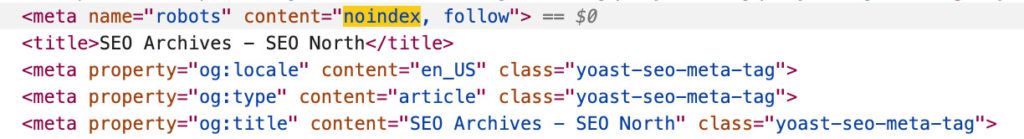
- Go to your WordPress dashboard navigate to ‘Appearance‘ > ‘Theme Editor.‘
- In the ‘Theme Files‘ section on the right, find and click on ‘header.php‘ to edit it.
- Locate the ‘robots‘ meta tag with the ‘noindex‘ directive in the code. It will look like this:
- <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, follow” />
- Remove the ‘noindex‘ part from the content attribute so it looks like this:
- <meta name=”robots” content=”follow” />
- Save the changes by clicking on the ‘Update File‘ button.
3. Check the Reading settings in WP
Ensure that the ‘Search Engine Visibility‘ option in the WordPress Reading settings is not enabled, as this will add a ‘noindex‘ directive to your entire website.
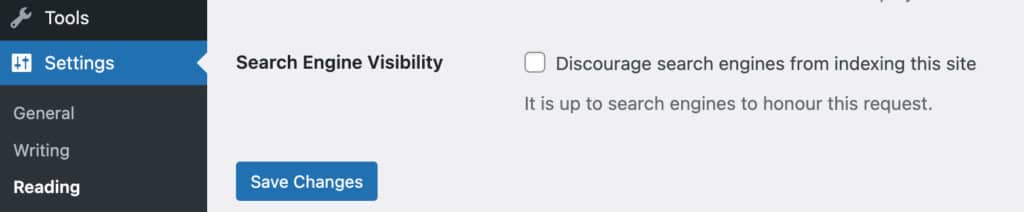
- Go to your WordPress dashboard navigate to ‘Settings‘ > ‘Reading.‘
- Scroll down to the ‘Search Engine Visibility‘ section and make sure the checkbox next to ‘Discourage search engines from indexing this site‘ is unchecked.
- Click on the ‘Save Changes‘ button.
After making these changes, the ‘noindex’ directive should be removed from the ‘robots’ meta tag. Keep in mind that it may take some time for search engines to crawl your site again and update their index. You can also request a re-crawl using Google Search Console to speed up the process.
Conclusion
Removing the ‘noindex’ directive from the ‘robots’ meta tag in WordPress can be achieved by checking and adjusting the settings of your SEO plugin, inspecting your theme’s header.php file, and ensuring that the ‘Search Engine Visibility’ option in the Reading settings is disabled. By following these steps, you can ensure that search engines index your WordPress website correctly, allowing it to appear in search results. Keep in mind that changes might take some time to be reflected in search engine indexes, so be patient and consider requesting a re-crawl through Google Search Console to expedite the process.If you are still uncertain about removing the noindex meta tag in meta robots, get a webmaster who offers services related to SEO and to help you manage your website hassle-free.
FAQ
How to remove noindex tag in Wordpress?
Published on: 2023-03-31
Updated on: 2024-07-15