Table of Contents
- Beginner’s Guide to SEO
- How Search Engines Work
- How Does a Search Engine Index and Rank Content?
- Different Search Engines Yield Better Results
- Can Search Engines Discover Your Site?
- Show the Search Engines the Right Way to Crawl Your Website
- Will Crawlers Find Your Most Important Content?
- Navigation Mistakes to Avoid
- Check Your Information Architecture
- Review Your Sitemaps
- Does Your Site Have Crawl Errors?
- How Your Site Is Indexed
- What Do My Pages Look Like to the Search Engines?
- Show the Search Engines How to Properly Index Your Site
- Learn About Different Robots Meta Tags
- How Do Search Engines Rank the Pages on Your Site?
- What About Engagement Metrics?
- Localized Search
- FAQ
- Did this article answer your questions?
Beginner’s Guide to SEO

Search engines are designed to find answers for internet users. They organize the internet so that you can instantly discover relevant search results. For your site to appear in the results, you have to get ranked in the search engine. This is why search engine optimization (SEO) is so important. You need top-notch SEO techniques if you want to be in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
How Search Engines Work
A search engine is made to crawl, index, and rank the internet. Crawling involves searching the web for content. The indexing process involves organizing the internet’s content. After indexing a page, it will appear as the answer to search queries. Then, the ranking process involves determining which pieces of content are the best results for specific queries.
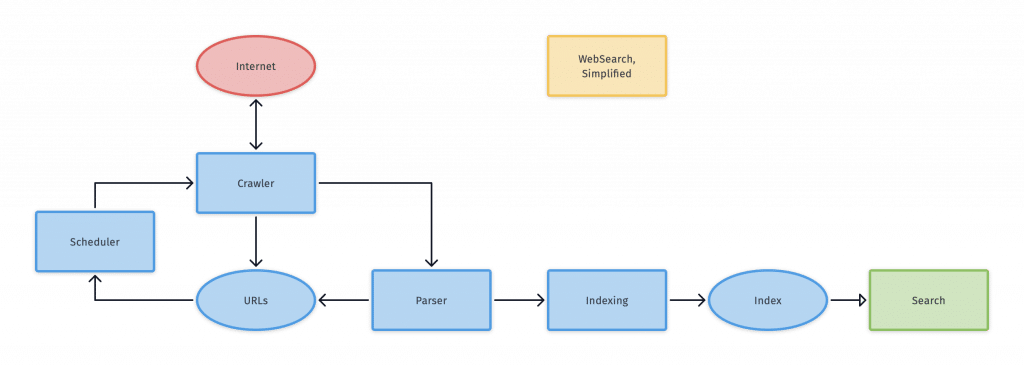
A search engine crawls a site and sends out search engine robots. These robots are also known as spiders. They crawl each content page by following links from certain pages to new URLs. When the spiders find new content, they give it to an index called Caffeine. This index is a database of URLs that can be retrieved by search engines whenever someone searches for something.
How Does a Search Engine Index and Rank Content?
A search engine’s index stores all of the content a search engine finds and stores. When someone types a search query, the engine searches through the index to find relevant content. The search engine ranks these results according to how relevant they are. A website with a high ranking means the search engine thinks it is more relevant than other results.
You can block web crawlers from going through your web pages if you want to. You can also tell the search engines to stop storing your pages in their index. Unless you have a reason to do this, you should avoid it. If search engines cannot crawl and store your pages, your pages are essentially invisible to the search engines.
Different Search Engines Yield Better Results
While they may look the same, the various search engines differ. Google possesses the largest portion of the marketplace, but more than 30 big search engines exist. Most content writers and website designers focus primarily on Google because 90 percent of searches happen on this site. It is 20 times larger than Yahoo and Bing combined.
Can Search Engines Discover Your Site?
If you want your site to appear in the SERPs, spiders must be able to crawl your pages. You can see if your site is crawlable by looking at how many of the site’s pages are included in the index. To do this, you can type “site:yourdomain.com” into the search bar on Google. The results are all the pages that Google has indexed from your site.
While the number of pages is not exact, it is a good reference point. You can try using Google Search Console’s Index Coverage report if you want extremely accurate results. This tool lets you submit a sitemap and quickly determine how many pages are included in Google’s index.
There are a few common reasons you might not appear in search engines.
- Your site is entirely new and has not gotten crawled yet.
- The site’s navigation makes it difficult for a robot to crawl your website.
- Your site is not linked to external sites yet.
- The search engines are penalizing you for spam-like tactics.
- Your site has crawler directives that stop search engines from crawling and indexing it.
Show the Search Engines the Right Way to Crawl Your Website
If your pages are not getting indexed properly, there are some steps you can take. You can tell Googlebot how you want it to crawl your content. While you want Googlebot to crawl most of your pages, there may be duplicate URLs, staging pages, and thin content that you do not want Googlebot to crawl.
Robots.txt
These files are placed in the site’s root directory as a suggestion to the search engines. They tell the search engines which pages they should crawl and how fast they should do it. When Googlebot does not see a robots.txt file, it crawls the entire site like normal. If it discovers a robots.txt file, it will generally listen to the suggestions in the file. When there is an error in the robots.txt file, it will not crawl the site at all.
Put Your Crawl Budget to Work
Your site has a crawl budget that determines how many URLs Googlebot will generally look at before it leaves. If you optimize your crawl budget, you can get Googlebot to crawl your most essential pages instead of your unimportant ones. Its crawl budget becomes incredibly important when a site has thousands or millions of URLs.
When you optimize your crawl budget, pay attention to noindex and canonical tags. You do not want to block web crawlers from pages with other directives. If you block Googlebot, it cannot see the canonical or noindex tags.
Some robots do not pay attention to robots.txt. Scammers and bad actors may even use robots.txt as a guide for finding where you have placed your private content. While blocking crawlers from login pages and private content seems intuitive, you should be cautious about doing this. You make their location public knowledge by putting these URLs in a robots.txt file. Instead, you should use noindex on these pages and add a login form.
Defining Your URL Parameters
Sites like e-commerce sites allow the same content to appear on various URLs by attaching certain parameters. For example, you can refine your search for coats on Amazon by selecting the coat’s size, style, brand, and color. The URL changes a little each time you refine your search.
While Google’s search engine is quite good at determining which URL is the best representative URL without help, you can assist search engines using Google Search Console’s URL Parameters feature. This feature lets you tell Googlebot to stop crawling URLs with specific parameters. In essence, you hide pages with duplicate content from the search engines.
Will Crawlers Find Your Most Important Content?
Keeping crawlers away from certain pages is helpful, but you also want Googlebot to find your essential pages immediately. You can achieve this goal by ensuring Googlebot can crawl through your site easily. Some sites are like a wall crawlers can reach, but they cannot go past the initial home page. If your content is hidden behind login forms, a crawler cannot access it.
What is the best way to provide a search engine with crawl instructions?
Creating a Sitemap is the best way to provide search engines with crawl instructions; recently updated articles and new pages are the web pages you want to be crawled first on your website. Sitemaps contain a list of URLs with the last modified date, providing search engines with a list of pages to be crawled.

Likewise, robots are unable to use search forms. They also cannot read non-text content like images. If the search engines want to understand your site’s images, you need to add text inside your web page’s HTML markup.
In addition, search engines must be able to follow a path of links from one page to the next. If a page is not linked to any other page, it is invisible to the search engines. You need to structure your navigation so crawlers can navigate easily.
- You should avoid having mobile and desktop navigation that show different results.
- Your navigation should have menu items in the HTML. For example, JavaScript-enabled navigation can still be difficult for a search engine to crawl and understand.
- Personalizing navigation for certain types of users can look like cloaking to Googlebot.
- If you do not link to primary pages on your website, crawlers cannot find them. Links are the primary way that crawlers get to new pages.
Check Your Information Architecture
Does your site use clean information architecture? Your information architecture is how website content is organized and labeled. Clean information architecture is intuitive for users, so they can efficiently find anything they want to.
Review Your Sitemaps
A sitemap is like a map to the URLs you have on your site. It shows Google which pages are the highest priority and which ones are unimportant. While you still need excellent site navigation, a sitemap helps crawlers determine which pages are the most important. You should make sure you only list URLs that you want indexed. If you do not have links from other sites yet, Google Search Console lets you submit an XML sitemap to get your site indexed.
Does Your Site Have Crawl Errors?
Ideally, crawlers should be able to see your site without any issues. You can visit Google Search Console if you want a Crawl Errors report. This report will tell you which URLs have issues. Your server log files also have this information, but beginners may find it challenging to access this log.
4xx Codes
These kinds of errors happen because of client errors. This means the requested URL cannot be fulfilled. It may also contain some wrong syntax. A 404 error is the most common type of error. It happens because there was a broken redirect, a deleted page, or a typo in the URL.
5xx Codes
These codes are server errors. They happen if the server does not fulfill the searcher’s request. These generally happen because the URL timed out, which means the bot quits trying to access the page.
Make a Custom 404 Page
You can improve your bounce rate with a customized 404 page. To do this, you have to add links to other important pages on your site or a search feature. Another option is to use a 301 redirect to send users from an old URL to a new one.

Create a 301 Redirect
You can use a 301 to boost link equity by transferring people from your old page to your new one. It also helps Google discover and index your new page. While 404 errors do not harm your overall performance, you can lose your ranking on those specific pages.
Because of this, you may want to use a 301 status code. It shows that the page has been permanently switched to a new location. Meanwhile, a 302 redirecting page represents a temporary move.
You need to avoid creating a redirect chain. Googlebot has problems going through multiple 301 status codes to reach a page. Because of this, you should stick to having just one redirect page as much as possible.
How Your Site Is Indexed
Your first goal is to make sure Google can crawl your sites. The next step is to get it indexed. Indexing is the way search engines store your pages. In essence, a search engine stores a rendering of your page like how a library stores a book.
What Do My Pages Look Like to the Search Engines?
You can easily see the latest cached version of each page of your site. When you check the SERPs, click the drop-down arrow by the page’s URL. Then, select the option for cached. Popular and established sites tend to be crawled and cached more frequently. You can also check out a text-only version of each cached page.
There are many reasons why an index might remove a page. The following are some of the most common reasons.
- The URL was penalized for a violation of the search engine’s guidelines.
- The URL has blocked crawlers because of a password requirement.
- The URL returns with a 4xx or 5xx error.
- The URL has a noindex directive.
You can try out the URL Inspection tool if you think there is a problem. You can also fetch the page as Google. Then, you can see if the page is getting appropriately rendered by Google.
Show the Search Engines How to Properly Index Your Site
Meta directives are also known as meta tags. These tags are instructions that tell the search engines how to look at your pages. You can create meta tags that stop search engines from being able to index a page. These instructions are generally placed in the head of your HTM pages or your X-Robots-Tag in your HTTP header.
Learn About Different Robots Meta Tags
Index/noindex: This tells the search engines whether or not to crawl the page.
Follow/nofollow: This shows whether bots should follow the links you have on your page or not.
Noarchive: This tells the search engines that they should not keep a cached copy of a specific page.
With meta directives, you can affect how your pages are indexed. They do not affect the way the pages are crawled. To follow the directive, the crawler must crawl the page to see them.
X-robots-tag: This tag can be placed in your URL’s HTTP header to block search engines.
How Do Search Engines Rank the Pages on Your Site?
Your ranking refers to how high your page is on the search engine results list. Most people click on the first three results, so your ranking determines the number of site visitors you receive. Search engines use formulas and algorithms to determine how information is stored. These search engine algorithms constantly change as Google works to improve search quality.
Search engines want to give searchers the best answers to their questions. Over time, search engines have become better at understanding semantics. While practices like keyword stuffing are used to trick search engines, the search engines are now capable of telling when a page is artificially stuffed with a keyword.
Links and SEO
Links are essential for SEO. Search engines look at your internal links and inbound links. Inbound links are the links you get from other websites that lead to your site. In a way, they are like an online version of word-of-mouth referrals. While search engines do not rely on these links as much as they used to, they still play a role in determining your search engine ranking. Google’s PageRank algorithm analyzes the quantity and quality of every link that goes to your pages.
Content and SEO
Content also plays a role in determining your search engine rankings. Crawlers scan your content to decide what your page is about. Then, it finds the most relevant content possible for each search query. Because the main goal is to achieve user satisfaction, there is no set rule about how long you should make your content.
RankBrain and SEO
Content, links, and RankBrain are the main factors determining how Google ranks your site. RankBrain involves machine learning. It can use observations to teach itself over time. Because it is constantly getting better, search results also improve. If one URL is more relevant to the search user, it will get a better ranking. This means that the best thing you can do is improve your user experience and make sure your content is relevant.
What About Engagement Metrics?
Engagement metrics are often higher for sites with a higher ranking, but there is a lot of debate about whether this is due to causation or correlation. Engagement metrics include clicks on your listing in search results, your bounce rate, and the time spent on your pages. The bounce rate is the percentage of sessions where the viewer only checks out one page before leaving.
Google has said that they use click data to adjust their SERPs. If most people click on the second result instead of the first result, Google will eventually switch the order of the results. This means that engagement metrics serve as fact-checkers for search engines. Crawlers can guess whether a page is relevant. Then, real visitors show Google which pages are relevant by clicking on them. If a page has a high bounce rate, it is probably not relevant for the searcher.
Localized Search
Google has experimented with a variety of search formats over time. This is intended to improve user experience by giving users the best type of content. With localized search, Google cares about relevance, distance, and prominence. To ensure you rank well, you should optimize your Google My Business listing.
Relevance means your business needs to match what the searcher wants. Meanwhile, distance involves your geo-location. Even though organic searches rarely broadcast this fact, they are generally influenced by the searcher’s location. Finally, Google wants to reward prominent businesses that are popular in the real world. They can tell if you have a well-known business by looking at your Google reviews and citations on other sites. In addition, Google will consider your other SEO techniques to determine your website’s position in a localized search.
FAQ
How do search engines work?
What is crawling and indexing?
What is the most common way a search engine discovers a web page?
What is the primary goal of a search engine?
What might help a search engine understand the difference between topics?
What might help a search engine understand the difference?
How do search engines crawl websites?
How will search engines deal with a poor site structure?
What is the average position in the Google Search Console?
What does a sitemap look like?
What is crawling in SEO?
What was the first search engine created?
Next: Keyword Research
Previous: SEO 101
Published on: 2020-09-10
Updated on: 2024-04-22