Technical SEO Optimization is an arduous and complex process, and it requires you to consider many factors such as content, user experience, site structure, page loading speed, and so forth. If you want your website to rank well in Google SERPs (search engine result pages), this article will help you.

Table of Contents
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing your website to help search engines as Google find, crawl, render, and index your web pages. The goal is to improve rankings.
Why Is Technical SEO Important?
Technical Search Engine Optimization is important because it ensures that your website is easy to navigate and free of any technical issues that prevent it from being understood or ranked by search engines.
It would help if you implemented Technical SEO to increase organic traffic and turn that traffic into customers. It also gives search engine algorithms reasons to trust your website.
How Can You Improve Your Technical SEO?
Technical SEO Audit Checklist
This checklist is aimed at beginners to help build a technical SEO strategy.
Crawling
XML Sitemap & Robots.TXT file
Create an XML sitemap & Setup a Robots.txt file; you can do this using Yoast Plugin on WordPress websites.
Canonical URLs
Check Canonical URLs – critical on e-commerce websites. You can perform this check by viewing your website’s code and ensuring it matches the current URL.
Fix Crawl Errors
Scan your website using crawler tools such as Screaming Frog (a free tool up to 500 pages), Ahrefs, and SEMrush to help Identify SEO issues for Crawl Errors using a site audit. You will want to fix excessive 3xx (redirects), 4xx (broken links), and 5xx (internal errors).
Check that you have a valid SSL certificate. You can do this by clicking on the lock symbol in your browser.
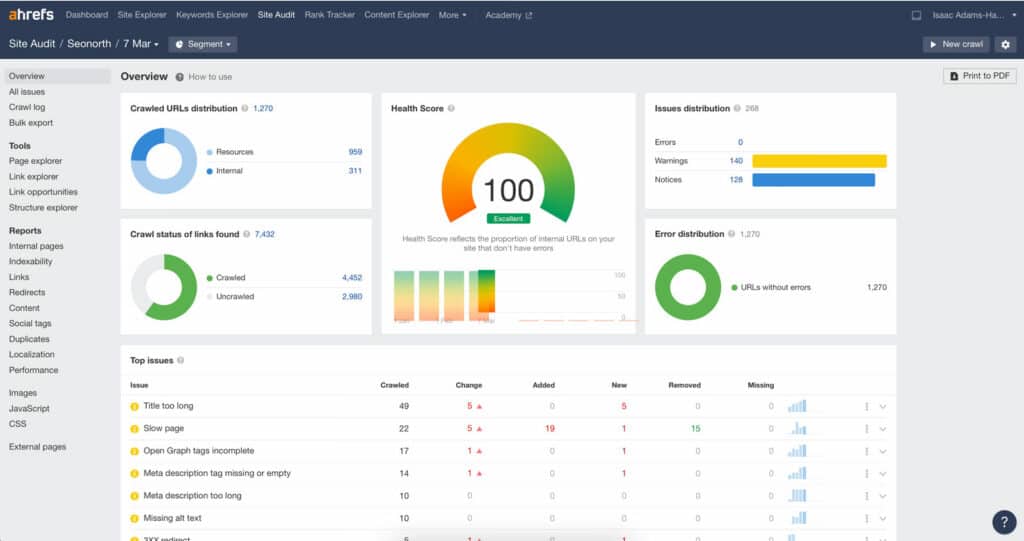
Mobile-Friendly tests
Run a Mobile-Friendly test; this is especially important with Mobile-first indexing. If you have any errors, Google Search Console will alert you. So it’s essential to have GSC adequately set up.
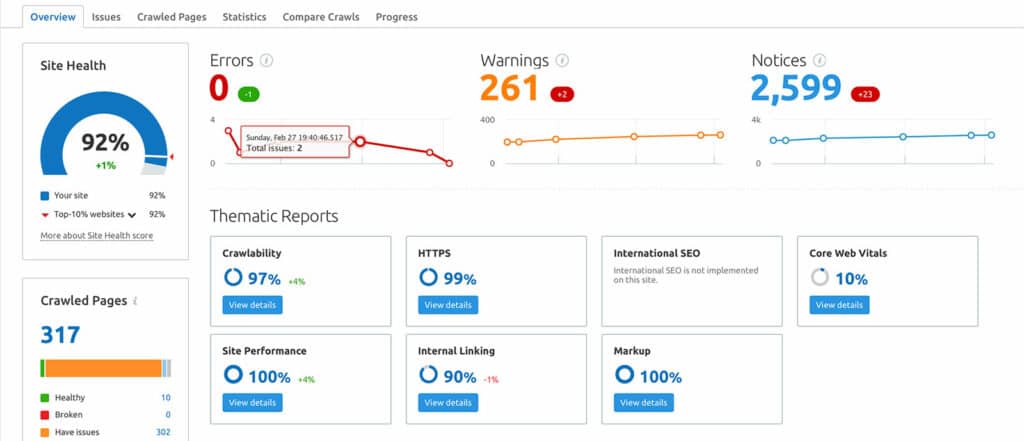
Site Structure
Optimize your Site Structure, ensuring all content is well organized (silo’d).
Add Internal linking; this process will help improve your PageRank score, help readers find related content, and maximize your crawl budget.
Before starting, to agree on a URL structure, it is crucial to have a consistent layout throughout the site.
Schema Markup
Add Schema Markup (structured data): Microdata & JSON-LD, Rich Snippets. You can automate this process using a Schema Plugin like Schema.press.
Site Speed
Test your site speed; you can perform this test using PageSpeed Insights or Google Analytics Site Speed Report. It’s crucial to install caching plugins, a CDN (content delivery network), and AMP (if desired) to improve load times. To improve the load speed, you can minify your HTML, CSS, and javascript themes.
Next, remove unused Plugins, and replace plugins with custom code where possible.
Setup Reporting
Set up Google Search Console (GSC) and Bing Webmaster Tools (BWT) to monitor rankings, and install Google Analytics (GA) to monitor traffic.
Historical Data
If you haven’t been a part of Search Engine Optimization from the start, check the website for anything that could be harming the website. This could be toxic backlinks from a black hat link-building campaign, mass amounts of content removal or even staging servers left indexed and active.

Rendering
Manual Testing
This part is primarily manual; spending time using the website is vital. Look for anything that could be holding it back regarding crawlers and users. Does it look great on a Desktop, Tablet, and is it Mobile-Friendly? For advanced users, you can run rendering tests using tools like BrowserStack.
Indexation
Content Optimization
Content optimization is key to success; you will want to continually improve your page’s content. Remove or fix duplicate content issues and thin content.
On-Page Optimization
If your site is new, focus on creating high-quality content, Optimize On-page SEO (title tags, h1s, metadata/meta-tags)
Google’s algorithms
It is essential to learn about Google Algorithms; it shows you areas to stay away from and how you can improve the technical aspects of your website.
- 2003 — Florida (anti-keyword stuffing spam)
- 2005 — Jagger (anti-link spam)
- 2009 — Caffeine (near real-time indexation)
- 2010 — MayDay (anti-thin content)
- 2011 — Panda (“quality”)
- 2011 — Google starts using SSL in search
- 2011 — Freshness (prioritizing fresh content)
- 2012 — Penguin (anti-link “spam”)
- 2012 — Knowledge Graph
- 2012 — EMD (exact match domain)
- 2013 — Phantom (quality update)
- 2013 — Hummingbird (core algorithm overhaul)
- 2015 — Rankbrain (contextual search)
The Takeaway
The most important takeaway to Technical SEO is that searchers and crawlers (Googlebot) can easily use your website without encountering errors.
Continue Learning
This page lists resources to provide you with the best information on optimizing your website for search engine optimization.
| TECHNICAL OPTIMIZATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| Overview of crawling and indexing topics | Guide | |
| The Beginner’s Guide to Technical SEO | Guide | Patric Stox / Ahrefs |
| What Is Technical SEO? Your Ultimate Guide To Getting Started | Guide | Kevin Indig / SEMrush |
| Technical SEO Guides Hub | Guide | ContentKing |
| The Ultimate Guide to Technical SEO | Guide | Christina Perricone / Hubspot |
| Technical SEO Library | Guide | Deep crawl |
| Technical SEO Audit (165+ Steps And Free Audit Template) | Guide | Olga Zarzeczna |
| Technical SEO course with Bastian Grimm | Course | Bastian Grimm / SEMrush |
| Large site owner’s guide to managing your crawl budget | Guide |
FAQ
What is technical SEO audit?
Published on: 2021-10-02
Updated on: 2024-06-21