If you’re a digital marketer or learning search engine optimization (SEO), then you’ve probably heard of Google’s PageRank. But what is it, exactly? And how can you use it to help your business? In this article, I’ll explain everything you need to know about PageRank, and I’ll provide some tips on how to improve yours. So read on for all the details!
Table of Contents
What is PageRank?
PageRank is a ranking algorithm used by Google Search to rank web pages in their search engine results (SERPs). It is named after the term “web page” and co-founder Larry Page. PageRank was developed by Google’s founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin at Stanford University to measure the importance of web pages.
Google’s PageRank Algorithm matters because it weighs the link structure of your website and determines where your site appears on Google search engine listings.
The Google search engine has two essential features that help it produce high-precision results. First, it uses the link structure of the Web to calculate a quality ranking for each web page. This ranking is called PageRank and is described in detail [Page 98]. Second, Google utilizes links to improve search results.
— The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine – Sergey Brin and Lawrence Page
Learning How Pages Score Rankings (simplified)
In simple terms, PageRank is like a popularity contest; some web pages can earn more votes from the PageRank Algorithm than others. The least popular contestant in PageRank’s score cannot be lower than one (1), while the highest PageRank value is ten votes (10). Hyperlinks create a vote for the recipient, and the vote counts more if the link comes from an authority web page.
The anchor text that matches search intent can add extra points, which helps a page earn a higher PageRank score.
How PageRank is Calculated (advanced)
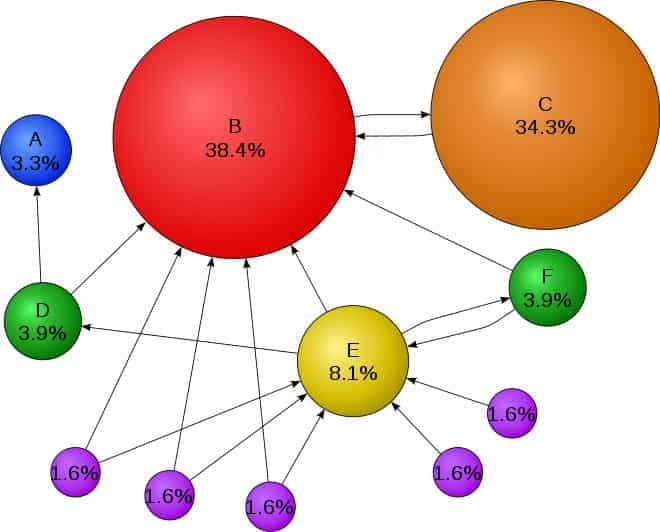
In the example above, Page C has a higher PageRank than Page E, even though there are fewer links to C; the one link to C comes from a significant page and is of high value.
Mathematical PageRanks for a simple network is expressed as percentages. (Google uses a logarithmic scale.) In the example above, Page C has a higher PageRank than Page E, even though there are fewer links to C; the one link to C comes from a significant page and is of high value. Using the PageRank calculation; If web surfers who start on a random page have an 82.5% likelihood of choosing a random link from the page they are currently visiting and a PageRank is expressed as percentages using a logarithmic scale. A logarithmic scale is a nonlinear scale often used when analyzing an extensive range of quantities. Instead of increasing in equal increments, each interval is increased by a factor of the logarithm base.
Using the PageRank calculation:
- If web surfers who start on a random page have an 82.5% likelihood of choosing a random link from the page they are currently visiting
- And a 17.5% likelihood of jumping to a page selected at random from the entire web
- They will reach Page E 8.1% of the time.
- The 17.5% likelihood of jumping to an arbitrary page corresponds to a damping factor of 82.5%.
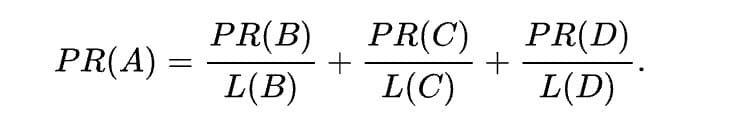
Without damping, all web surfers would eventually end up on Pages A, B, or C, and all other pages would have a PageRank of zero. In the presence of damping, Page A effectively links to all pages on the web, even though it has no outgoing links of its own.
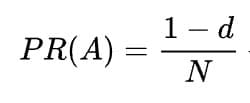
Where A, B, C, and D are pages, L is the number of links going out from them, and N is the total number of pages in the collection (i.e., on the Internet).
As you can see, PageRank uses the web’s link structure to calculate a quality ranking for each web page. The homepage would naturally have a higher PageRank score since all pages link to the homepage. It also shows you why you wouldn’t want to link the bottom of every article to the contact us page.
The PageRank formula uses a random surfer model that reaches its target site after several clicks and then switches to a random page to calculate the chances of a person clicking on a link.
A-PageRank or PR(A) can be calculated using a simple iterative algorithm and corresponds to the principal eigenvector of the normalized link matrix of the web.
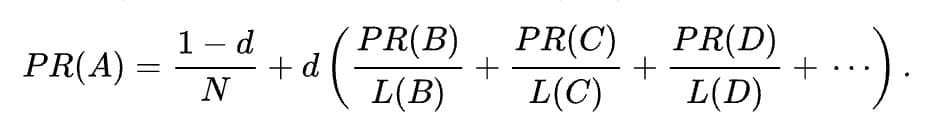
The eigenvalue problem was suggested in 1976 by Gabriel Pinski and Francis Narin, who worked on scientometrics ranking. Eigenvectors are a particular set of vectors associated with a linear system of equations (i.e., a matrix equation) that are sometimes known as characteristic, proper, or latent vectors.
The PageRank computations require several passes, called “iterations,” through the collection to adjust approximate PageRank values to more closely reflect the actual theoretical value.
Error tolerance is used to check convergence in the power method solver.
Creating Link Juice to Improve PageRank
Back to the simplified explanation, backlinks that send traffic to your website add a vote in your favor. Link juice (a slang word used for PageRank) increases the tally of references to your site, and they work for internal or external links. The number of links and authority of these links are calculated to give you a PageRank score. Internal links distribute Link Juice to pages on your website.
Ranking factors that govern the link authority that influences your score and PageRank include quality and quantity. Creating high-quality content increases the chances that webmasters will create outgoing links to your web page. However, since PageRank works on a logarithmic scale, only a limited number of links will account for added value. Therefore, when your site links to external pages, each receives an equal share of the votes or points.
Enhancing Your Score
Many factors influence your PageRank score; below are some steps to increase the probability of a higher PageRank value.
Internal link Optimization
While not as effective as external links, internal link optimization is imperative when implementing an effective SEO strategy. In addition to enhancing the flow of the crawlers through your site, it can improve your PageRank value. Internal links signals to Google Search which pages are the most important.
Create links more Clickable
Links with a higher chance of users clicking on them usually have a higher value (due to the random surfer model). The potential for click-ability governs the value that a click receives. You can enhance the probability by creating links higher in the article, adding bolding, larger or different font, and better calls to action for these links.
Optimizing Anchor Text
Anchor text tells search engines and users what the hyperlink is about. It would be best to have a good idea of what page you will be redirected to when clicking on links. Well-chosen anchor text, when used sparingly, can help your page achieve better search results. Google does not respond well to keyword stuffing anchor text tactics; use different keywords instead of repeating the same one, generating better results. The text before and after the hyperlink can evaluate the link value.
Discouraging Google from Following
NoFollow links prevent(ed) the flow of PageRank until recently when this became a hint. Historically, SEOs sometimes used the NoFollow attribute to sculpt the flow of PageRank.
In addition, links that appear in sponsored content need a sponsored attribute, and user-generated content (UGC) should have a UGC tag to comply with Google’s policies.
HTML Link Examples:
<a rel=”sponsored” href=”https://example.com/seo”>matt cutts</a>
<a rel=”ugc” href=”https://example.com/wiki”>Wikipedia</a>
<a rel=”nofollow” href=”https://example.com/vendor”>Outbound links</a>
Seeking High-quality Backlinks
Backlinks that point to your website from a high-quality website will increase your PageRank score. However, the better the backlink, the harder they are to acquire. Nevertheless, these high-quality backlinks contribute significantly to the ranking of your website, making them worth the effort to gather as many as you can. As a critical factor in establishing the value of your site, they stand above many others.

Backlinks matter to SEO performance, and link building provides an opportunity to influence your ranking as you enhance traffic to your site. Just as two sides of a coin give a compliment to the other, effective backlinks and polished SEO practices do the same thing. Therefore, both deserve your attention to become proficient, and practicing with the proper approach can provide valuable results.
Takeaway
We might not have a Google PageRank toolbar anymore (to find your PageRank score), but that doesn’t mean we don’t need to understand how PageRank scoring works and the factors that influence it; it’s one of the key factors in SEO success. If you want help growing your pages PageRank score naturally while also taking advantage of modern search engines optimization (SEO) techniques like keyword research and content marketing, then send me a DM on LinkedIn.
